Building Event-Driven Microservices - Chapter 13 - Integrating Event-Driven and Request-Response Microservices

How to integrate event-driven microservices with request-response APIs?
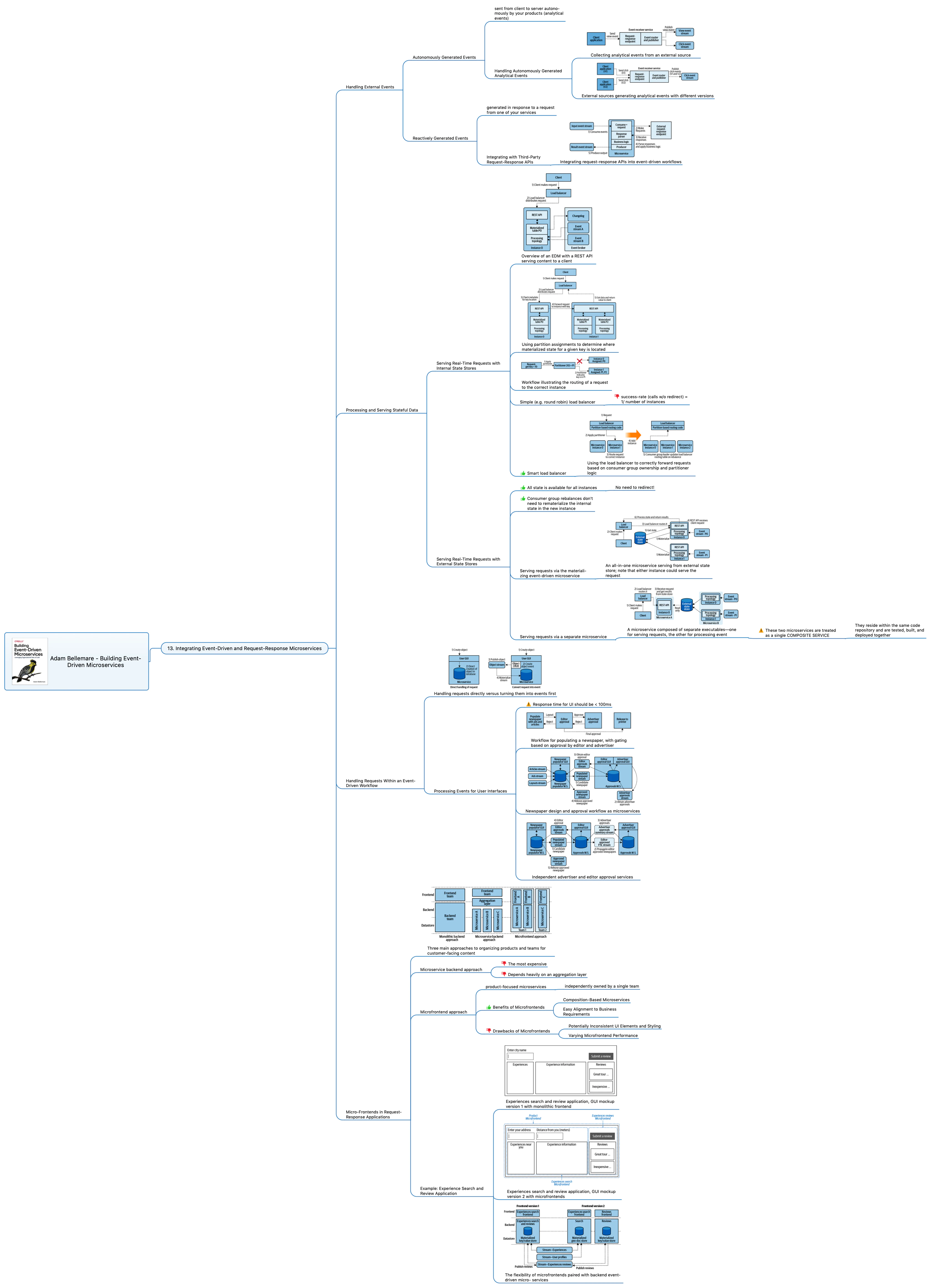
There are two types of external events:
- Autonomously Generated Events (analytical events)
- Reactively Generated Events (events from request-reply)
There are two approaches of processing and serving requests using stateful services:
- using internal state stores (with silly or with smart routing)
- using external state stores (with regular or with composite microservice)
Ways of handling requests within an event-driven workflow:
- Handling requests directly
- Turning requests into events (big latency)
- Processing events for user interfaces (a mix of two ways)
Approaches for request-response applications, their pros and cons:
- Monolithic backend approach
- Microservice backend approach
- Microfrontend approach
All of these is disclosed in the Chapter 13 of the book we are currently studying:
“Building Event-Driven Microservices: Leveraging Organizational Data at Scale” by Adam Bellemare
Sharing my mind map with all the details as usual:
See also:
- Building Event-Driven Microservices - Chapter 7 - Stateful-Streaming
- Building Event-Driven Microservices - Chapter 12 - Lightweight Framework Microservices
- Building Event-Driven Microservices - Chapter 11 - Heavyweight Framework Microservices
- Building Event-Driven Microservices - Chapter 10 - Basic Producer and Consumer Microservices
- Building Event-Driven Microservices - Chapter 9 - Microservices Using Function as a Service