Building Event-Driven Microservices - Chapter 5 - Event-Driven Processing Basics

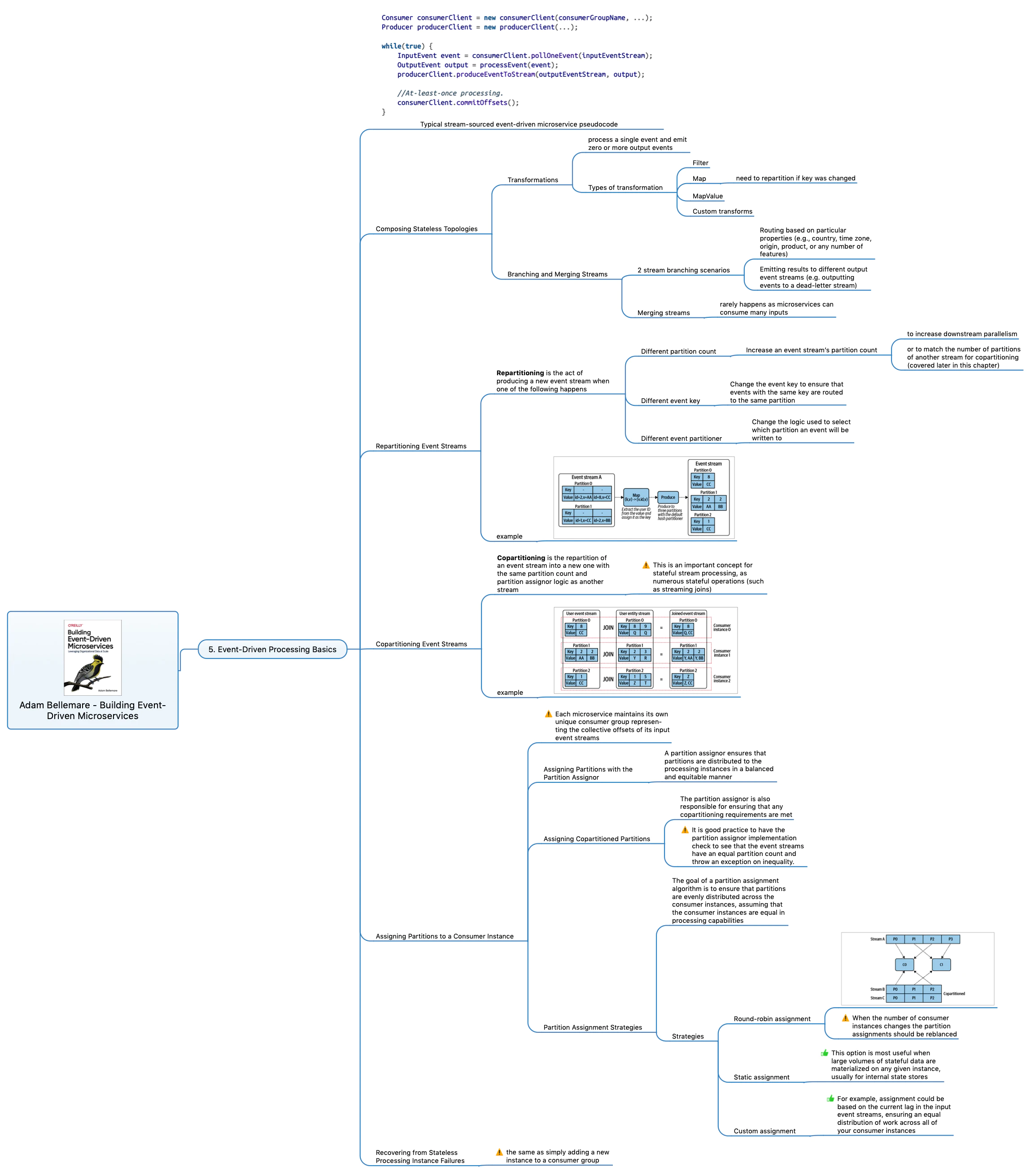
Overviewing basics of event processing in Event-Driven Architectures:
- Typical structure of microservice
- Typical types of event transformations, 2 branching scenarios, merging streams
- Repartitioning events and when it can be useful
- Copartitioning events and when it is needed
- Assigning Partitions to a Consumer Instance. Three strategies to do this.
- Recovering from stateless processing instance failures.
These topics are disclosed in the Chapter 5 of the book we are currently studying:
“Building Event-Driven Microservices: Leveraging Organizational Data at Scale” by Adam Bellemare
Sharing my mind map with all the details as usual:
See also:
- Building Event-Driven Microservices - Chapter 12 - Lightweight Framework Microservices
- Building Event-Driven Microservices - Chapter 2 - Event Driven Microservice Fundamentals
- Building Event-Driven Microservices - Chapter 15 - Testing Event Driven Microservices.
- Building Event-Driven Microservices - Chapter 13 - Integrating Event-Driven and Request-Response Microservices
- Building Event-Driven Microservices - Chapter 11 - Heavyweight Framework Microservices