Justice - 05 - Markets and Morals

In the next two lections of JUSTICE you dive into the intriguing debates on military conscription, personal choice, and patriotism. Then explore the ethical dilemmas of surrogacy, consent, and commodification in the riveting. Uncover the limits of government power and the complexities of reproductive technology in these captivating discussions.
I am sharing my mind-map from the lectures as usual:
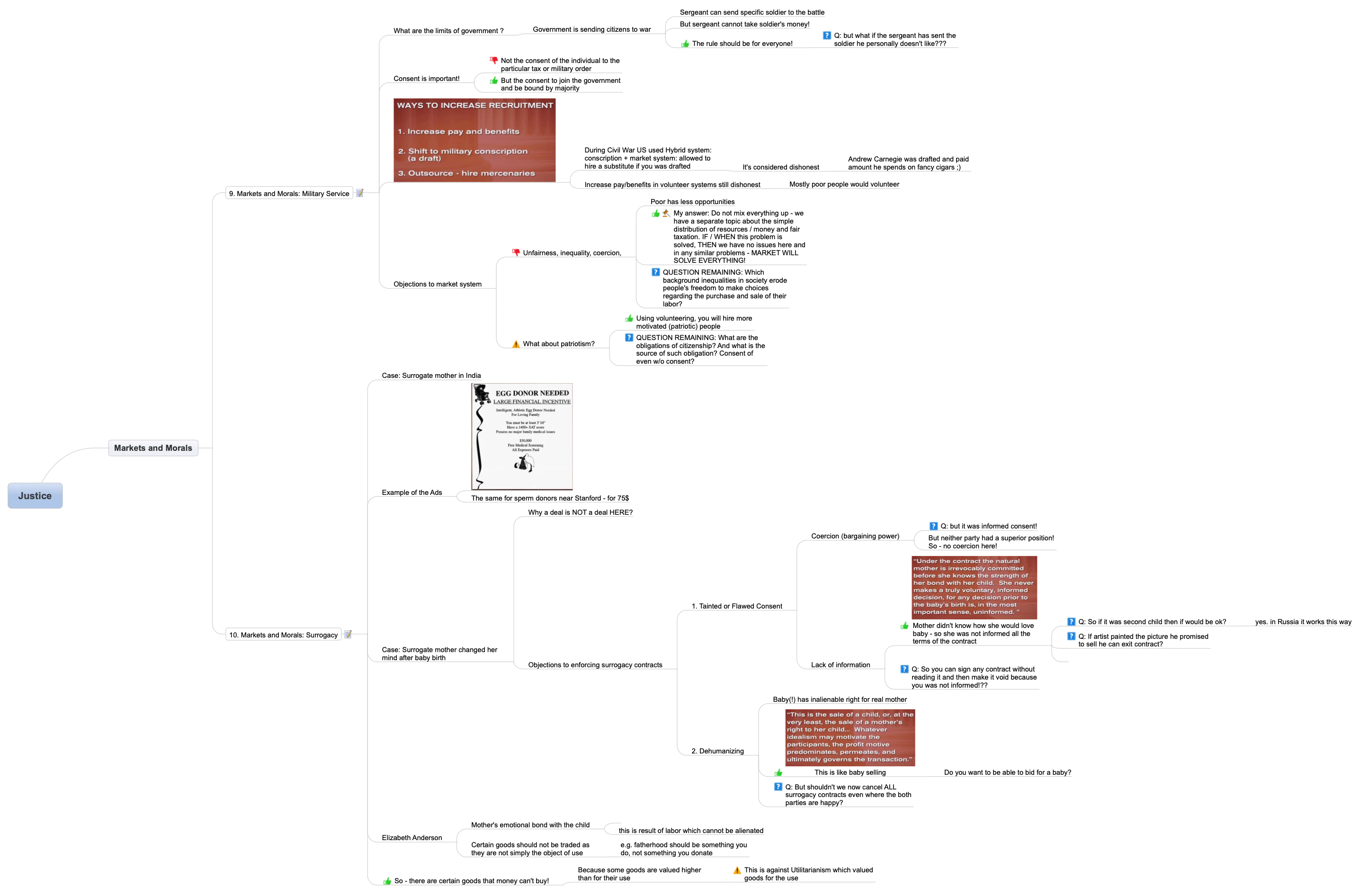
Summary of the lectures:
Lecture 9. Markets and Morals: Military Service
The lecture explores Locke’s concept of government by consent, which allows democratically elected governments to tax citizens with prior consent. However, there are limits to government power, which even the agreement of the majority cannot override. The discussion then shifts to military conscription, with some arguing that it violates the right to self-possession. The lecture provides three solutions to the military recruitment problem faced by the United States during the Iraq War, including increasing pay, conscription, and outsourcing. The Civil War system, which combined conscription with a buyout provision, is also discussed. The discussion then focuses on the differences between the conscription system in the Civil War and the all-volunteer military system today, with some arguing that the latter is more just because it allows individuals to choose whether to serve. However, others argue that conscription would make the entire country feel a sense of responsibility for conflicts. Finally, the debate touches on whether patriotism or money is a better motivation for serving in the military.
Lecture 10. Markets and Morals: Surrogacy
The lecture delves into the controversies surrounding reproductive technology, specifically the buying and selling of eggs and sperm, as well as surrogacy. The speaker discusses the various levels of compensation for egg and sperm donors and the contract dispute that arose in the Baby M case, which involved commercial surrogate motherhood. The audience is asked whether they believe the contract should have been enforced, and the majority agrees that it should have been upheld. However, objections to surrogacy are raised, including the issue of tainted consent and the commodification of babies. The New Jersey Supreme Court ruled that the surrogacy contract was unenforceable due to lack of fully informed consent and the unacceptable commodification of the child. The lecture examines the arguments against surrogacy and assesses their persuasiveness.
Links: